INTEGERATED SERVICES
A. Introduction To Topic
B. Advantages of having single
ISPN
C. Type of Real Time applications
1. Intolerant and Rigid.
2. Tolerant
and Adaptive
D. Architecture
and mechanism of ISPN
1.
Service Interfaces.
2.Scheduling
Policies.
(Guarantted services,predicted services,Integerated
services).
3. Nature
of committment.
4.Means by which
committment is to be fulfilled.
Introduction
to topic:
The two traditional networks i.e Telephone
network and Computer Networks were designed for different purposes.Telephone
network is meannt for passsing voice and computer networks are
meant for passing data.However now they is no well defined boundary
as telephone networks are using computer networks for passing there
voice data and compter networks are using telephone networks to provide
user internet services.But when voice service is provided by computer
networks and data service is provided by telephone networks the condition
becomes worse because they are not meant for that purpose for which
we are using them.So there is a great need of a network which can provide
data services as well as provide supports for eral time applciations.So
a new network ISPN jas been proposed which carry data in digital
form and have support for every type of service.So we have Integerated
Service Network.Some may say why to have one single network for every
type of service but having a single network offers a multitude of advantages.
Advantages
of having single ISPN :
following are the advantages of having single network
:
1. Economy
of scale.
2. ubiquity
.
3. Easy
connectivity to any network any where in world.
4. More
stress will be on how to ensure peer to peer connection
ispite of stressing on how the data will flow between hetrogeneous
networks.
5. Design
of gateways will become simple.
and many more.
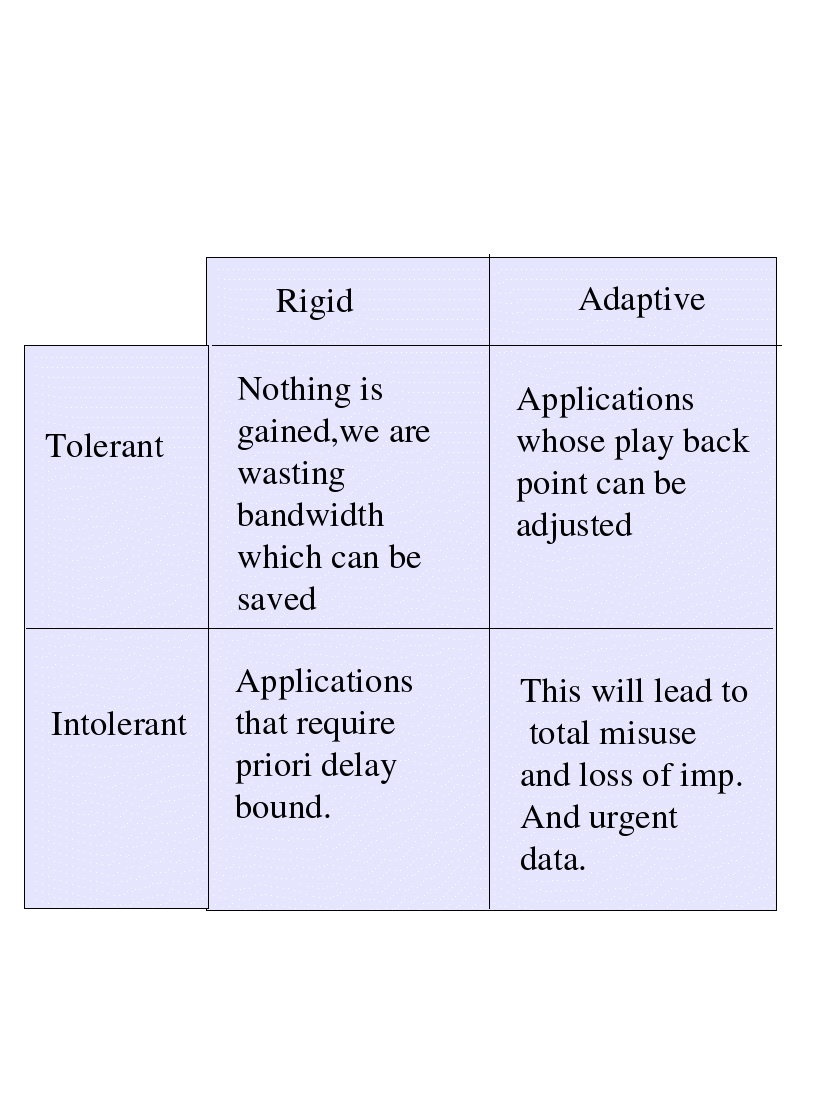
Types of real time
applications :
They are classified on the basis of their working.In
real time applications we set a play back point and all the packets
are allowed to store in a buffer of suitable size at the receiver
and then all the packets which are stored in the buffer and received
before play back point are taken and rest of the packets are ignored.It
is the position of the play back point and its variation dynamically
that classifies the Real Time Applications.There are certain applications
which requires a particular bound which is precalculated and in no
case the bound should exceed that, for these type of applications
play back point is fixed .However we have certain applications that can
bear a little bit of delay and so for these applications we can shift
play back point depending on the present conditions of the network.so
we have two type of applications
1. Rigid : In these applications
w have priori bound and a fixed play back point which does not vary
during connection and these are generally guaranteed services.
2. Adaptive applications
: In these application depending on the current conditions of the
network and studying how much delay network is offering to different
packets , play back point is adjusted.So if load is less on network
or number of flows are less then play back point will come down and
if the load is very high than play back point moves up but there
is certain maximum value of play back point and in no case the play back
point can become greater than that otherwise at the receiver end
we will get nothing but the noise.
These nature of applications are combined with
one another nature of being tolerant and intolerant which is defined
as :
1. Tolerant applications
: These are the applciations which are tolerant to some extent i.e
there is a certain range between which play back point
can vary and so play back point can be adjusted for these applications
dynamically depending on the load of network.
2. Intolerant applications
: These are the applications which have a strick delay which can't
be excedded and should not be excedded in any case for e.x if we
have surgeon which is doing operation and getting tips from a senior
surgeon than in this case we can't shift play back point because
if we do so and then there is sudden increase in load in network
and most of the packets will be delayed and it result in the
form of noice or silence at the receiver.So for these applications
we have a fixed delay bound on the packets .
These two classifications of applicatiosn
are combined so as to get one specific form classification of applications
:
Architecture
and mechanism :
The most important part of any
new system is its architecture which is backbone of it and the mechanism
that is used to provide desired services that are the commitments of this
new system to its user.So architecture of the ISPN includes four parts :
1. Service Interfaces:
The most
important part in this ISPN network is that how it will provide interfaces
to different types of services.Network should know about the charactersitics
of traffic from a particular sender and about different parameters and
how to handel this type of traffic.So the different types of services(which
largely guodes the charactersitic of traffic) can be classified as below.
a.. Guaranteed services : In
this type of service network has priori information about the traffic which
it is going to receive from the sender and network has provision to handel
that type of traffic.So if the sender fulfills his commitment by providing
that type of trafic then network will fulfill its commintment by sending
data to destination in the desired bound.
b. Predicted services :
In this service the network makes a assumption that past is the guide
to the future.so depending on the present conditions , the network shedules
the packet i.e if the load is less than it sends packets at the faster
rate but the assumption is that the conditions should remain same after
that if there is shift from present condition of the network than it can
result in loss of important data.So in the predicted services network tries
to minimize delay by taking some risk.
How these services are handled
or in general traffic of these services are handle depend on the scheduling
policies, the scheduling policy is used at intermediate routers to route
the packet to proper destination and also the scheduln decision is made
based on the information contained in the packet header.So the algorithm
should be such that it should not take much of processor time otherwise
lot of time of processor is utilized in doing scheduling and it will result
in unnecessary delay of packets.
2. Nature of commitments :
This includes
what are the commitmens made by the network to the users.So commitments
includes the transfer of data from any sender to proper destination within
the bounds and ISPN fulfill its commitment by dividing the service provided
to the users in to two types i.e guaranteed services and predicted services.
3. Scheduling policies :
Scheduling policies are used to
schedule the packets of a particular traffic from sender to proper destination.ISPN
uses a scheduling policiy which can be used for guaranteed traffic and
predicted traffic.So ISPN uses an integerated policy that can be used
for any type of traffic and is thus universal and supports evry type of
aplications inlcuding Real time applications.
So scheduling policy which is used is
based on the scheduling policies used for the guaranteed service and predicted
service which are :
a. WFQ(wighted Fair Queuing).
b. FIFO.
c. priority queuing (Enhancement of both these methods ).
(Do google search on Queuing
methods)
WFQ(Weighted Fair
Queuing) :
This method which is used for guarantted traffic is based on the traffic
filter that is there is bucket for every flow on aline that specifies how
fast the user corresponding to that flow can send the data and how fast
the network can handle the data.This traffic filter thus can be used for
giving priority to a particular flow over others .
This traffic filter
is actually a bucket having following charactersitics :
b= bucket size.
r= token filling rate of bucket.
So a traffic filter
is characterize on the basis of (r,b).
Every packet which is to be send from a particular queue has to take
equivalent number of tokens from the bucket.So if we have a packet of size
p then when it is send then p tokens are consumed from bucket.
So number
of tokens present in bucket for sequence ni is given by :
ni=MIN[ b, ni-1 + (ti - ti-1)
* r - pi]
and n0=b.
Here b specifies
the burstiness of the flow becuase it is the maximum size of the packet
which can be transferred at a particular time.ni specifies the
number of tokens which are left in the bucket after ith packet leaves and
for a given traffic we can specify the increasing
function b(r) so that process conforms to [r,b(r)] filter.
The wighted fair queuing method is used for guarantted
traffic because it keeps isolation between the different flows and if one
flow is bursty than it will not going to affect other flows and the affect
will be on oinly this flow.However it will many times lead to inefficient
utilization of bandwidth because if some flow is not using its share fully
than that share can be utilized by the bursty flow , however it may be
possible in case or predicted service but it is not good for guaranteed
services in which a poor application may also affect some good applications.
Parekh and Gallager said:
if flow get same clock rate at all
routers(clock rate of a particular flow is the share of link given to that
flow) and capacity of total flows is less than link capacity
capacity of total flows < link
capacity
than network delay is bounded by (b(r) / r).
FIFO fair queuing method:
WFQ is suitable for guaranteed
services but it is not perfect for predicted services and reason is that
it provides isolation between the different flows.However in case of FIFO
there is statistical sharing and that provides lot of advantages because
burstiness can be handled to a large extent.If some flow is bursty than
delay is equally transferred to all flows and hence bursty data can be
handled with less delay.
PRIORITY CLASSES :
In this method we have priority classes
for different services and every priority classes have certain number
of flows.In this method isolation is prvided between the flows which are
in the same class but the traffic can be transferred from the flow belonging
to higher priority class to the flow belonging to the lower priority class.
References :
1. Assigned
Reading for this lect. notes.
2. Lecture
presentation.
