Scribe Notes For Lecture 32
By
Kuldip Patel
Y3111029
kuldip@iitk.ac.in
Circuit Switching
vs Packet Switching
In a circuit switched network there is a physical end to end connection
created between the communicating parties.
This connection is maintained for the duration of the call and is of a
fixed data rate. The PSTN (telephone network) is the classic example.
Circuit-switched networks require dedicated
point-to-point connections during calls.
In Circuit
swithcing state per connection is maintained so it is limited to scaling.
In packet switching there is no
dedicated end to end connection between communicating parties.
Individual packets are treated separately. The
data rate can vary.
Voice connections - circuit switched is ok
(circuit has a high percentage of utilisation because somebody is
generally always talking!)
With data connections the line is frequently
idle, e.g. surfing the Web! We don’t need a circuit-switching approach
because it is inefficient.
- Circuit switching uses up the whole capacity of the line!
- Packet switching allows hosts to share the line!
Packet switching is used to optimise the
use of the bandwidth available in a network and to minimise the latency.
Packets are routed to their destination
through the most expedient route.
Not all packets travelling between the same
two hosts will necessarily follow the same route.
The destination computer reassembles the packets
into their appropriate sequence.
It is connection-less, like IP
Packet Switching is Destination based routing hence it is slower.
MPLS
It stands for
Multi-Protocol Label Switching.
It is the
latest technique that provides virtual path capability to packet(label)
switches.
Motivation
To avoid some
drawbacks of both circuit switching and packet switching and to increase
the utilization of bandwidth MPLS came into picture.
MPLS is
basically to manage the traffic within the ISP .
It combines the
benifits of both Circuit switching and packet switching .
It uses Circuit
switching within ISP. and IP based packet switching within ISPs.
The idea behind MPLS is to attach a discrete set of labels to IP
packets to perform a specific function, without forcing routers and
switches to dive into IP addresses or other information in each packet
to obtain instructions relating to that particular function.
MPLS packet
Forwarding
MPLS does Label
switching in which label is assigned to each IP flow.
It direct a
flow of IP packets along a predetermined path across a network.
This path is
called a label-switched
path (LSP).
LSPs are
simplex; that is, the traffic flows in one direction from the head-end
(ingress) router to a tail-end (egress) router.
Duplex traffic
requires two LSPs: one LSP to carry traffic in each direction.
An LSP is
created by the concatenation of one or more label-switched hops,
allowing a packet to be forwarded from one router to another across the
MPLS domain.
When an ingress
router receives an IP packet, it adds an MPLS header to the packet and
forwards it to the next router in the LSP.
The labeled
packet is forwarded along the LSP by each router until it reaches the
tail end of the LSP, at which point the MPLS header is removed and the
packet is forwarded based on Layer 3 information such as the IP
destination address.
Here the label
not the Destnation IP address determine the next route.
MPLS HEADER AND
PACKET FORMAT
MPLS
Header
MPLS Header is
32-bit.
Label
(20-bit)->First 20-bits are to specify Label per flow.
CoS(Class of
Service (3bit)-> It is proposed to use is to indicate perhop
behavior of labeld packet traversing Label Switch Routers.
Stack bit->
Indiacte the presence of Label Stack.
TTL(8-bit)->
It is Time To Leave filed , decremented at each LSR hop and used to
throuw away the looping packets.
Label
(20 bit)
|
Cos(3bit)
|
S |
TTL(8-bit)
|
MPLS
Packet.
MPLS fits
between Layer 2 and Layer 3.
L2
Header
|
MPLS
Header
|
L3
Header
|
L3 Data
|
L2
Header
|
MPLS
Header
|
MPLS
Header
|
L3
Header
|
L3 Data
|
MPLS Path Recovery
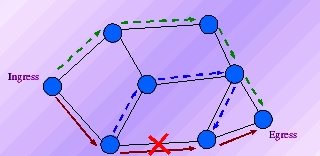
Figure 1.
Suppose There
is a link failure ,as shown in figure, on the path from ingress router
to egress router then there are 2 ways of replacing it.
Local Recovery(green in figure):-Choose alternate
path between 2 LSR which were connected by teh failed link. It enables a
router upstream from the failure to route around the failure quickly to
the router downstream of the failure. The upstream router then signals
the outage to the ingress router, thereby maintaining connectivity
before a new LSP is established.
End
to End recovery(blue in figure):- Use an Alternate
path from Ingress router to Egress Router.In Later option there is some
propagation dealy to know the link failure.
Detecting such
a failure is by insertion of some kind of periodic keep alive in the
data path of the LSP (Note that keep alives such
as OSPF hello,
RSVP refresh etc. Monitoring the presence of these keep alives at
downstream nodes.
All this needs
extra processing.
Features
- (MPLS) traffic engineering software enables an MPLS
backbone to replicate and expand upon the traffic engineering
capabilities of Layer 2 ATM and Frame Relay networks.
- Traffic engineering is essential for service provider and
Internet service provider (ISP) backbones. Such backbones must support a
high use of transmission capacity, and the networks must be very
resilient, so that they can withstand link or node failures.
- MPLS traffic engineering provides an integrated approach to
traffic engineering. With MPLS, traffic engineering capabilities are
integrated into Layer 3, which optimizes the routing of IP traffic,
given the constraints imposed by backbone capacity and topology.
- MPLS traffic engineering routes traffic flows across a network
based on the resources the traffic flow requires and the resources
available in the network.
- MPLS traffic engineering employs "constraint-based routing," in
which the path for a traffic flow is the shortest path that meets the
resource requirements (constraints) of the traffic flow.
- MPLS traffic engineering gracefully recovers to link or
node failures that change the topology of the backbone by adapting to
the new set of constraints.
What is Lembda MPLS
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) promises to improve the
performance, reliability and service quality in packet-switched networks
by bringing many of the advantages of ATM networks to an arbitrary
switched link layer while avoiding many of their disadvantages. MPLS
achieves this by taking advantage of existing routing protocols to set
up virtual label-switched paths across a set of label switching routers
to identified destinations, thus requiring a packet's layer 3 header to
be interpreted only at the ingress and egress of an MPLS switching
domain. This not only reduces the packet-processing overhead but allows
for multiple paths to be established for a single destination. It allows
the support for path protection, segregation of traffic by class
of service and traffic engineering.
Multiprotocol Lambda Switching extends this paradigm into the optical
domain by using an extended MPLS (or MPLS-like) control plane to control
optical cross-connects. In effect instead of "route once switch many"
we then have "electrical once, optical many" or "switch once, then
transmit".
��This lambda switching technology is an offshoot of an important
traffic-engineering technique called Multi-protocol Label Switching.
They share the same acronym and are almost the same thing, only with
wavelengths substituting for numerical labels in the lambda version.
